Email marketing has long been one of the most powerful tools for businesses to reach their audience. However, simply sending generic emails to your entire list is no longer effective.
With customers becoming more discerning, expecting tailored content, and receiving a higher volume of messages, businesses need to get smarter about how they communicate.
This is where email segmentation comes into play. Segmenting your email list allows you to send highly targeted, relevant messages that resonate with specific groups of subscribers.
It’s no longer just about sending an email to “everyone”—it’s about sending the right message to the right person at the right time.
In this article, we’ll explore key email segmentation strategies that can help maximize engagement, increase open and click-through rates, and ultimately drive conversions.
1. What is Email Segmentation?
Email segmentation is the process of dividing your email list into smaller, more targeted groups based on shared characteristics, behaviors, or demographics. The goal is to send personalized content that is relevant to each group, increasing the likelihood that they’ll engage with the email and take the desired action.
Segmentation can be based on various factors, including:
- Demographics (age, gender, location)
- Purchase behavior (frequency, recency, amount spent)
- Engagement history (opens, clicks, inactivity)
- Customer lifecycle (new subscribers, repeat buyers, loyal customers)
- Interests and preferences (based on preferences or browsing history)
By leveraging segmentation, you can tailor your email marketing strategy to speak directly to your audience’s unique needs, wants, and behaviors.
2. Why is Email Segmentation Important?
Effective segmentation is key to improving the success of your email marketing campaigns. Here are several reasons why it matters:
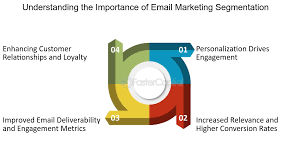
a) Improved Relevance
Sending emails tailored to specific segments increases the relevance of your content. When recipients receive emails that directly address their needs, interests, or behaviors, they are more likely to open, read, and act on your emails.
b) Higher Engagement Rates
Personalized and relevant emails see higher engagement rates. Emails with targeted content—whether based on location, behavior, or previous interactions—lead to better open rates, click-through rates, and more conversions.
c) Better Conversion Rates
Segmentation allows you to send the right message at the right time. For example, sending a special offer to a customer who abandoned their cart is far more effective than sending the same offer to your entire list. This leads to higher conversion rates and a better return on investment (ROI).
d) Increased Customer Retention and Loyalty
By sending the right message to the right person at the right time, segmentation fosters better relationships with your customers. This helps build trust and loyalty, which can lead to repeat purchases, referrals, and long-term customer retention.
3. Key Email Segmentation Strategies
Now that we understand the importance of segmentation, let’s explore some of the most effective strategies for dividing your email list and sending targeted content.
a) Demographic Segmentation
Demographics are some of the most basic but valuable data points for segmentation. You can divide your audience based on characteristics like age, gender, location, income level, job title, and more. These factors often influence purchasing decisions, making demographic segmentation a powerful tool for personalizing content.
Examples:
- Location-based segmentation: If you have a global audience, you can send location-specific offers or event invitations.
- Example: “Hi [Name], we’re offering free shipping on all orders within [City].”
- Age or life stage: Tailor content for different age groups. For example, marketing to millennials may differ from targeting baby boomers.
- Example: “Summer essentials for every generation – check out our styles for young adults.”
b) Behavioral Segmentation
Behavioral segmentation is one of the most powerful strategies in email marketing. By tracking your customers’ behavior, such as what they’ve bought, what they’ve clicked on, or how they’ve interacted with past emails, you can segment your list into highly targeted groups. This allows you to send relevant messages that align with their interests or actions.
Examples:
- Purchase history: Segment based on what customers have bought in the past and offer relevant upsells or cross-sells.
- Example: “Thanks for purchasing [Product]. You might also like these related items.”
- Website activity: If a customer browsed a specific category or product but didn’t purchase, send a follow-up email to encourage them to complete the purchase.
- Example: “You left some amazing items in your cart – come back and finish your order!”
- Email engagement: Segment based on how often recipients engage with your emails, such as those who open every email, those who rarely open, and those who never engage.
- Example: “We miss you! Come back and see our latest updates with a 20% discount.”
c) Lifecycle Segmentation
Lifecycle segmentation targets customers at different stages of their journey with your brand. By understanding where each subscriber is in the customer lifecycle—whether they’re a new subscriber, first-time buyer, repeat customer, or loyal advocate—you can send content that is tailored to their current needs.
Examples:
- New subscribers: Send a welcome series to introduce them to your brand and offer incentives like a first-time discount.
- Example: “Welcome to [Brand]! Here’s 10% off your first purchase.”
- First-time buyers: Follow up with a thank-you email and offer related products to encourage repeat business.
- Example: “Thanks for your purchase, [Name]! Here are some items you might love based on your order.”
- Loyal customers: Send exclusive offers or loyalty rewards to customers who have bought from you multiple times.
- Example: “You’re one of our top customers! Enjoy 15% off your next order as a thank you.”
d) Engagement-Based Segmentation
Engagement-based segmentation groups subscribers by their level of interaction with your emails. This is especially helpful for re-engagement campaigns. By segmenting based on email opens, clicks, and past interactions, you can target dormant or low-engagement subscribers with specialized content.
Examples:
- Highly engaged subscribers: Send them advanced offers or exclusive content, such as a VIP program or early access to sales.
- Example: “As a loyal subscriber, you’re the first to know about our newest collection—check it out!”
- Inactive subscribers: Send re-engagement emails with a special offer to win them back.
- Example: “We miss you! Here’s 20% off to welcome you back.”
- One-time subscribers: Nurture subscribers who have signed up but never engaged with your emails. Send helpful or educational content to re-engage them.
- Example: “Still interested in [topic]? Here are some resources we think you’ll love.”
e) Psychographic Segmentation
Psychographic segmentation dives into customer lifestyles, values, interests, and attitudes. While this requires more effort to collect and analyze, it can result in highly personalized campaigns that resonate deeply with your audience.
Examples:
- Interest-based segmentation: If a subscriber has shown interest in certain product categories (e.g., fitness, travel, fashion), segment them accordingly to send highly relevant content.
- Example: “Since you love outdoor adventures, check out our newest camping gear.”
- Survey-based segmentation: Use surveys to collect information about your customers’ preferences and segment your list accordingly.
- Example: “What’s your favorite way to unwind? Take our short survey and get personalized product recommendations.”
f) Transactional Segmentation
Transactional segmentation groups customers based on their purchase history, including frequency, value, and recency of purchases. This type of segmentation helps you target high-value customers with exclusive offers, while also re-engaging customers who haven’t made a purchase in a while.
Examples:
- Frequent buyers: Send loyalty rewards or early access to new products.
- Example: “Thank you for being a loyal customer! Here’s 20% off your next purchase as a token of our appreciation.”
- Infrequent buyers: Target customers who have made one or two purchases with a special offer to encourage them to return.
- Example: “It’s been a while since your last purchase! Enjoy 15% off to complete your order.”
- High-value customers: Reward high-spending customers with exclusive deals or VIP programs.
- Example: “You’re part of our elite club! Enjoy free shipping and a special gift with your next purchase.”
4. Best Practices for Email Segmentation
- Start simple: Begin with basic segmentation based on demographics or engagement, and then expand as you gather more data.
- Use advanced tools: Leverage advanced email marketing platforms that provide segmentation features and automated workflows (e.g., Klaviyo, ActiveCampaign, or Mailchimp).
- Test and optimize: Regularly test your segmented campaigns to see which segments respond best and refine your strategy over time.
- Respect privacy: Always ask for consent when collecting data, and be transparent about how you use it. Make sure to comply with privacy regulations like GDPR.
Conclusion: Transform Your Email Marketing with Segmentation
Email segmentation is one of the most effective strategies for improving the relevance and success of your email marketing campaigns.
By dividing your email list into targeted groups based on demographic, behavioral, lifecycle, and transactional data, you can send highly personalized messages that drive higher engagement, conversions, and customer loyalty.
Start implementing segmentation today and watch your email marketing evolve from generic mass emails to highly relevant, effective, and impactful campaigns that resonate with your audience.